The Rules of Backgammon: Complete Guide to Understanding This Strategy Game
Our online backgammon is one of the oldest and most captivating board games. This strategic game combines thinking, luck, and competition in a simple yet engaging format. Played on a distinctive board, it pits two players against each other as they move their checkers (known as “stones”) based on the roll of two dice. The objective is to remove all your stones from the board before your opponent does.
In this article, we’ll explain the rules of backgammon in a detailed and clear manner. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced player, you’ll discover everything you need to know about playing backgammon.
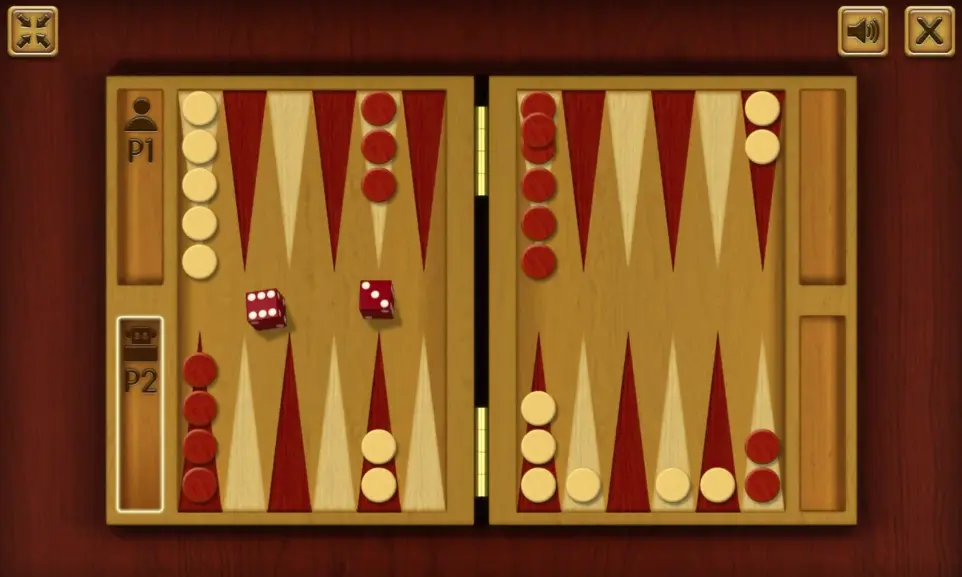
1. Introduction to Backgammon
Backgammon is a two-player game where each aims to move their 15 checkers around the board to remove them in a designated area called the “home.” The game is played using dice and a board divided into 24 triangles called points.
This game is ideal for those who enjoy combining strategy and anticipation. It requires both planning and effective management of opportunities created by dice rolls.
2. The Board and Game Materials
To play backgammon, you’ll need:
- A board divided into four quadrants containing 24 triangles (points).
- 30 checkers: 15 for each player, typically in contrasting colors (e.g., black and white).
- Two standard dice to determine movements.
- A doubling cube used to multiply points during betting (in certain variants).
Zones on the Board:
- Home board: The quadrant where checkers must be brought before being removed.
- Outer board: The quadrant adjacent to the home board.
- Bar: The central line dividing the two sides of the board, where captured checkers are placed.
- Points: The triangles numbered 1 to 24. Each player follows a specific order of movement.
3. Initial Checker Setup
At the start of the game:
Each player places their 15 checkers on specific points of the board:
- 2 checkers on point 24,
- 5 checkers on point 13,
- 3 checkers on point 8,
- 5 checkers on point 6.
4. How to Play Backgammon
A game of backgammon alternates turns between two players. On each turn, a player rolls the dice to determine their moves.
a) Rolling the Dice
- Each player rolls two dice at the beginning of their turn.
- The results indicate how many points the player can move their checkers.
- If both dice show the same value, this is a “double,” allowing the player to make four moves of the rolled value instead of two.
b) Moving Checkers
- Checkers move along a predefined path, from the opponent’s outer board to their own home board.
- Moves can only be made to open points—those that do not contain more than one opponent’s checker.
- Players can split their dice rolls between two checkers or use them for a single checker.
5. Captures and Checkers on the Bar
When a player lands on a point occupied by a single opponent checker, that checker is captured and placed on the bar.
a) Returning to the Board
- A captured checker must re-enter the game before the player can move other checkers.
- To re-enter, the player must roll a dice value corresponding to an open point in the opponent’s home board.
6. Bearing Off Checkers and Winning
Once all a player’s checkers are in their home board, they can begin removing them.
a) Conditions for Bearing Off
- The dice roll must match a point containing a checker. If there are no checkers on the indicated point, the player can remove a checker from a further point.
b) Winning the Game
- The first player to remove all their checkers wins the game.
7. Advanced Rules and Variants
Backgammon offers various optional rules and variants for added depth and strategy:
a) The Doubling Cube
- Used to raise the stakes of the game, the doubling cube allows a player to multiply the points in play when they feel confident.
- The opponent can either accept the double or forfeit the game.
b) Gammon and Backgammon
- A player who finishes the game without the opponent bearing off a single checker scores a Gammon (double points).
- If the opponent has checkers in the home board or on the bar, this results in a Backgammon (triple points).
8. Strategies for Success in Backgammon
While dice rolls are part of the game, good strategy can make all the difference.
a) Control Strategic Points
- Occupy key points (like points 5 or 7) to block your opponent’s movements.
b) Play Defensively
- Avoid leaving single checkers on the board, as they’re vulnerable to capture.
c) Capitalize on Doubles
- Doubles offer an opportunity to advance quickly. Plan your moves to make the most of these rolls.
d) Block Opponent’s Checkers
- Build walls of checkers (called “anchors”) to slow your opponent’s progress.
9. Benefits of Playing Backgammon
Backgammon offers more than just entertainment:
a) Improves Strategic Thinking
- It enhances skills in planning, decision-making, and risk management.
b) Social Interaction
- It’s a great game to enjoy with family or friends.
c) Versatile Gameplay
- With numerous variants, it can be played casually or competitively.
10. History of Backgammon
Backgammon is one of the oldest board games, with origins dating back over 5,000 years. Similar games have been found in Mesopotamia and Ancient Egypt.
In its modern form, backgammon became popular in Europe in the 17th century and spread worldwide due to its simplicity and universality.
Conclusion
Backgammon is a timeless and engaging game, perfect for strategy enthusiasts. With simple yet strategic rules, it provides unparalleled gameplay enjoyment. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced player, take the time to understand the nuances of backgammon and start playing today.
Whether for casual games with friends or competitive tournaments, backgammon continues to captivate players worldwide with its iconic board and gameplay.
